静态链接&动态链接
iOS AOP文章系列
前导知识:
- Mach-O文件结构分析
- 静态链接&动态链接
- OC方法&OC类&OC对象
- 方法查找和消息转发
AOP框架:
- Method Swizzling
- Fishhook
- Apsects
- NSProxy AOP
静态链接
还是通过 🌰 来分析:
➜ ios cat bar.c
int global = 1;
void fizz(int a) {
global = a;
}
➜ ios cat main.c
extern int global;
void fizz(int a);
int main() {
fizz(100 + global);
return 0;
}
编译链接 bar.c 和 main.c 生成可执行文件 main
➜ ios xcrun -sdk iphoneos clang -c bar.c main.c -target arm64-apple-ios13.4
➜ ios xcrun -sdk iphoneos clang bar.o main.o -o main -target arm64-apple-ios13.4
我们看下链接前后符号表的变化:
➜ ios jtool -S bar.o
0000000000000000 T _fizz
0000000000000020 D _global
➜ ios jtool -S main.o
0000000000000000 T _main
U _fizz
U _global
➜ ios jtool -S main
0000000100000000 T __mh_execute_header
0000000100007f54 T _fizz
0000000100008000 D _global
0000000100007f74 T _main
U dyld_stub_binder
在链接前 bar.o 中 fizz 和 global 符号地址为临时地址,main.o 中 main 符号为临时地址,fizz 和 global 符号未定义,静态链接为可执行文件 main 后,发现各符号都有了对应地址,这中间发生了什么呢?
其中关键就是符号的解析和重定位。
用 MachOView 查看 main.o 文件:

代码中符号的位置用 global 和 fizz 暂时用0x0和0x2c替代,链接器在完成地址空间分配后,就可以确定符号的虚拟地址了,链接器根据符号地址对每个需要重定位的指令进行地址修正,通过 _text 头中可以看到需要重定位的有三处以及重定位表偏移(488 = 0x1E8)。

而具体重定位信息在重定位表 Relocations 中:

重定位表结构为:
struct relocation_info {
int32_t r_address; /* offset in the section to what is being
relocated */
uint32_t r_symbolnum:24, /* symbol index if r_extern == 1 or section
ordinal if r_extern == 0 */
r_pcrel:1, /* was relocated pc relative already */
r_length:2, /* 0=byte, 1=word, 2=long, 3=quad */
r_extern:1, /* does not include value of sym referenced */
r_type:4; /* if not 0, machine specific relocation type */
};
其 r_symbolnum 具体为 Symbol 符号表中 index

符号表是一个数组,元素结构为 nlist_64:
struct nlist_64 {
union {
uint32_t n_strx; /* index into the string table */
} n_un;
uint8_t n_type; /* type flag, see below */
uint8_t n_sect; /* section number or NO_SECT */
uint16_t n_desc; /* see <mach-o/stab.h> */
uint64_t n_value; /* value of this symbol (or stab offset) */
};
链接后(main)的符号表,其 n_value 已经替换为真实地址:

动态链接
静态链接是运行前就用 ld 链接器链接成一个完整的程序,而动态链接是程序主模块被加载时候,通过 dyld 加载命令,把 dylib 加载到内存,然后将程序中所有未决议的符号绑定到相应的 dylib 中,并进行重定位工作。
动态链接器加载命令 LC_LOAD_DYLINKER:

动态链接库加载命令 LC_LOAD_DYLIB:

还是用之前的 🌰 ,但是我们通过动态链接库生成可执行文件 main_dyld
➜ ios xcrun -sdk iphoneos clang -c main.c -o main_dyld.o -target arm64-apple-ios13.4
➜ ios xcrun -sdk iphoneos clang -fPIC -shared bar.c -o libbar.dylib -target arm64-apple-ios13.4
➜ ios xcrun -sdk iphoneos clang main_dyld.o -o main_dyld -L . -l bar -target arm64-apple-ios13.4
我们查看 main_dyld 的符号表,发现并没有真实地址,但是标记了该符号来自动态库 libbar.dylib:

我们跟踪 _TEXT,__text 看下 global 变量 和 fizz 函数是如何重定位的

global 是通过 adrp 和 ldr 指令间接寻址,取0x100008000里面的值,而这个地址指向的 got(也称 Non-Lazy Symbol Pointers ) 表中:

在程序装载过程中,会重定位 got 表中地址,但是如何知道这是什么符号?以及这个符号来自哪里?
这就需要用到 Section64 Header(__got) 中的 reserved1 字段,它代表在间接符号表(Indirect Symbols)中的 index

而间接符号表本身存的是符号表中的 index,可以看到 index=1 的项值为4,代表符号表中 index=4 的项


22代表在 String Table 中偏移22的字符串,即为 _global,并且描述 _global 来自 libbar.dylib 动态库,解决了上述两个问题,现在可以重定位 got 表中第一个符号地址。
在看下 fizz 函数的重定位过程
bl #0x100007f88
指向 _stubs 符号桩中

➜ ios otool -v main_dyld -s __TEXT __stubs
main_dyld:
Contents of (__TEXT,__stubs) section
0000000100007f88 nop
0000000100007f8c ldr x16, #0x4074 ; Latency: 4
0000000100007f90 br x16
0x7f8c + 0x4074 = 0xc000
指向 __la_symbol_str 数据段

同样我们根据 Section64 Header(la_symbol_str) 中的 reserverd1 能够知道其符号名为 _fizz,而该函数的具体实现指向了 0x7fac (stub_helper 桩代码段)

通过 b #0x100007f94 跳到节头地址,然后走到 br x16 ,x16 为存储 0x1000080008 在的 dyld_stub_binder 函数

这个我们在Mach-O文件结构分析中已经讲过,是一个延迟绑定的过程,第一次调用外部函数,会调用 dyld_stub_binder 函数去寻址函数地址,然后写入 __la_symbol_str 段,之后再调同样的函数就会直接访问函数实现地址。我们看下 dyld_stub_binder 具体源码实现:
#if __arm__
/*
* sp+4 lazy binding info offset
* sp+0 address of ImageLoader cache
*/
.text
.align 2
.globl dyld_stub_binder
dyld_stub_binder:
stmfd sp!, {r0,r1,r2,r3,r7,lr} // save registers
add r7, sp, #16 // point FP to previous FP
ldr r0, [sp, #24] // move address ImageLoader cache to 1st parameter
ldr r1, [sp, #28] // move lazy info offset 2nd parameter
// call dyld::fastBindLazySymbol(loadercache, lazyinfo)
bl __Z21_dyld_fast_stub_entryPvl
mov ip, r0 // move the symbol`s address into ip
ldmfd sp!, {r0,r1,r2,r3,r7,lr} // restore registers
add sp, sp, #8 // remove meta-parameters
bx ip // jump to the symbol`s address that was bound
#endif /* __arm__ */
调用 fastBindLazySymbol 函数,该函数也可以在 git 上找到:
uintptr_t fastBindLazySymbol(ImageLoader** imageLoaderCache, uintptr_t lazyBindingInfoOffset)
{
uintptr_t result = 0;
// get image
if ( *imageLoaderCache == NULL ) {
// save in cache
*imageLoaderCache = dyld::findMappedRange((uintptr_t)imageLoaderCache);
if ( *imageLoaderCache == NULL ) {
const char* message = "fast lazy binding from unknown image";
dyld::log("dyld: %s\n", message);
halt(message);
}
}
// bind lazy pointer and return it
try {
result = (*imageLoaderCache)->doBindFastLazySymbol((uint32_t)lazyBindingInfoOffset, gLinkContext,
(dyld::gLibSystemHelpers != NULL) ? dyld::gLibSystemHelpers->acquireGlobalDyldLock : NULL,
(dyld::gLibSystemHelpers != NULL) ? dyld::gLibSystemHelpers->releaseGlobalDyldLock : NULL);
}
catch (const char* message) {
dyld::log("dyld: lazy symbol binding failed: %s\n", message);
halt(message);
}
// return target address to glue which jumps to it with real parameters restored
return result;
}
真正进行符号绑定的操作在 doBindFastLazySymbol 中:
uintptr_t ImageLoaderMachOCompressed::doBindFastLazySymbol(uint32_t lazyBindingInfoOffset, const LinkContext& context,
void (*lock)(), void (*unlock)())
{
// <rdar://problem/8663923> race condition with flat-namespace lazy binding
if ( this->usesTwoLevelNameSpace() ) {
// two-level namespace lookup does not require lock because dependents can't be unloaded before this image
}
else {
// acquire dyld global lock
if ( lock != NULL )
lock();
}
const uint8_t* const start = fLinkEditBase + fDyldInfo->lazy_bind_off;
const uint8_t* const end = &start[fDyldInfo->lazy_bind_size];
if ( lazyBindingInfoOffset > fDyldInfo->lazy_bind_size ) {
dyld::throwf("fast lazy bind offset out of range (%u, max=%u) in image %s",
lazyBindingInfoOffset, fDyldInfo->lazy_bind_size, this->getPath());
}
uint8_t type = BIND_TYPE_POINTER;
uintptr_t address = 0;
const char* symbolName = NULL;
uint8_t symboFlags = 0;
long libraryOrdinal = 0;
bool done = false;
uintptr_t result = 0;
const uint8_t* p = &start[lazyBindingInfoOffset];
while ( !done && (p < end) ) {
uint8_t immediate = *p & BIND_IMMEDIATE_MASK;
uint8_t opcode = *p & BIND_OPCODE_MASK;
++p;
switch (opcode) {
case BIND_OPCODE_DONE:
done = true;
break;
case BIND_OPCODE_SET_DYLIB_ORDINAL_IMM:
libraryOrdinal = immediate;
break;
case BIND_OPCODE_SET_DYLIB_ORDINAL_ULEB:
libraryOrdinal = read_uleb128(p, end);
break;
case BIND_OPCODE_SET_DYLIB_SPECIAL_IMM:
// the special ordinals are negative numbers
if ( immediate == 0 )
libraryOrdinal = 0;
else {
int8_t signExtended = BIND_OPCODE_MASK | immediate;
libraryOrdinal = signExtended;
}
break;
case BIND_OPCODE_SET_SYMBOL_TRAILING_FLAGS_IMM:
symbolName = (char*)p;
symboFlags = immediate;
while (*p != '\0')
++p;
++p;
break;
case BIND_OPCODE_SET_TYPE_IMM:
type = immediate;
break;
case BIND_OPCODE_SET_SEGMENT_AND_OFFSET_ULEB:
if ( immediate >= fSegmentsCount )
dyld::throwf("BIND_OPCODE_SET_SEGMENT_AND_OFFSET_ULEB has segment %d which is too large (0..%d)",
immediate, fSegmentsCount-1);
address = segActualLoadAddress(immediate) + read_uleb128(p, end);
break;
case BIND_OPCODE_DO_BIND:
result = this->bindAt(context, address, type, symbolName, 0, 0, libraryOrdinal, "lazy ", NULL, true);
break;
case BIND_OPCODE_SET_ADDEND_SLEB:
case BIND_OPCODE_ADD_ADDR_ULEB:
case BIND_OPCODE_DO_BIND_ADD_ADDR_ULEB:
case BIND_OPCODE_DO_BIND_ADD_ADDR_IMM_SCALED:
case BIND_OPCODE_DO_BIND_ULEB_TIMES_SKIPPING_ULEB:
default:
dyld::throwf("bad lazy bind opcode %d", *p);
}
}
if ( !this->usesTwoLevelNameSpace() ) {
// release dyld global lock
if ( unlock != NULL )
unlock();
}
return result;
}
这里通过 __LINKEDIT 段的基地址 + Lazy Binding Info 偏移(LC_DYLD_INFO_ONLY 加载命令中)计算 Lazy Binding Info 地址
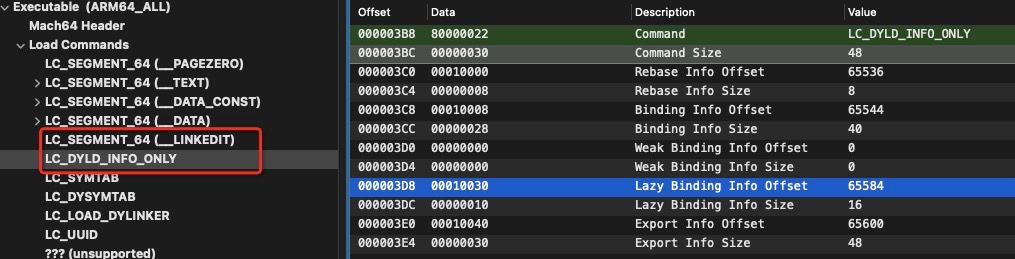
并通过函数在表偏移定位具体函数信息,看到 _fizz 是在 libbar.dylib 动态库中,待改写的区域为 __DATA.__la_symbol_str
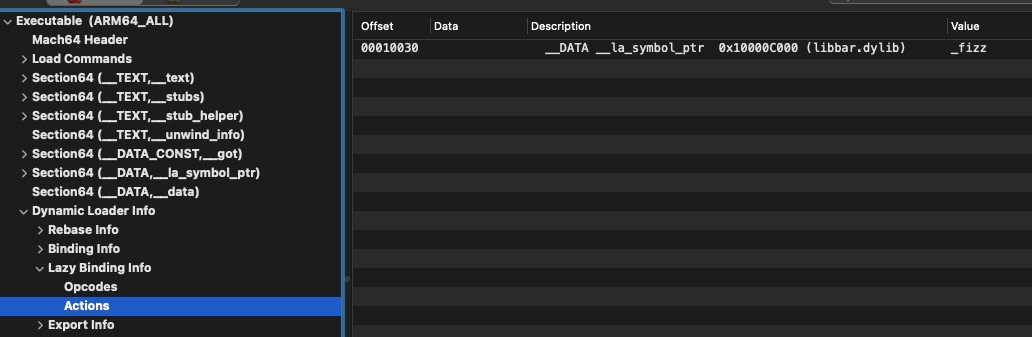
最后调用 bindAt 方法通过符号名在目标库中获取函数真实地址,并调用 bindLocation 方法改写 __la_symbol_str 中指向。
uintptr_t ImageLoaderMachOCompressed::bindAt(const LinkContext& context, uintptr_t addr, uint8_t type, const char* symbolName,
uint8_t symboFlags, intptr_t addend, long libraryOrdinal, const char* msg,
LastLookup* last, bool runResolver)
{
const ImageLoader* targetImage;
uintptr_t symbolAddress;
// resolve symbol
symbolAddress = this->resolve(context, symbolName, symboFlags, libraryOrdinal, &targetImage, last, runResolver);
// do actual update
return this->bindLocation(context, addr, symbolAddress, targetImage, type, symbolName, addend, msg);
}
动态链接的过程就结束了,这其中涉及到几个关键原理和概念:
- 相对寻址和间接寻址
PIC原理- 延迟绑定
got和la_symbol_ptrdyld动态链接
PIC原理
上述 global 和 fizz 两个符号是在动态库中,而动态库是可以被多个进程共享的,而动态库编译时不知道自己在进程中的虚拟内存地址,因此动态库中不能包含绝对地址,那动态库如何将代码段做到与位置无关共享出去,就需要将对地址的引用分离,放到主程序数据部分(可修改),在加载和运行过程做寻址绑定操作。
got 和 la_symbol_ptr
通过上述分析,我们可以看到动态库数据 (global) 地址放到 got (Non-Lazy Symbol Pointers) 数据段,非惰性代表动态链接阶段就寻找好所有数据符号的地址;而函数 (fizz) 用了延迟绑定技术,将外部函数地址放在 la_symbol_ptr (Lasy Symbol Pointers) 数据段,惰性的,程序第一次调用到这个函数才寻址真实地址并写入这个数据段。